-
article · 2025Year57Moon22Day
如何利用 Flex 实现蛋白质样品的高通量纯化?
Read More -
article · 2025Year16Moon20Day
Opentrons Flex 的自动吸光度读板机使用技巧有哪些?
Read More -
article · 2025Year13Moon19Day
Flex 的磁力模块能处理哪些复杂样品?
Read More


As a key tool for accurately transferring liquids in the laboratory, pipettes' accuracy and reliability are directly related to the accuracy and repeatability of experimental data. In order to ensure that pipettes maintain high accuracy during long-term use, it is particularly important to formulate and implement a set of scientific and standardized standard operating procedures for pipette calibration. This procedure aims to guide laboratory workers to correctly perform pipette calibration through detailed steps and strict standards, thereby ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experimental results.
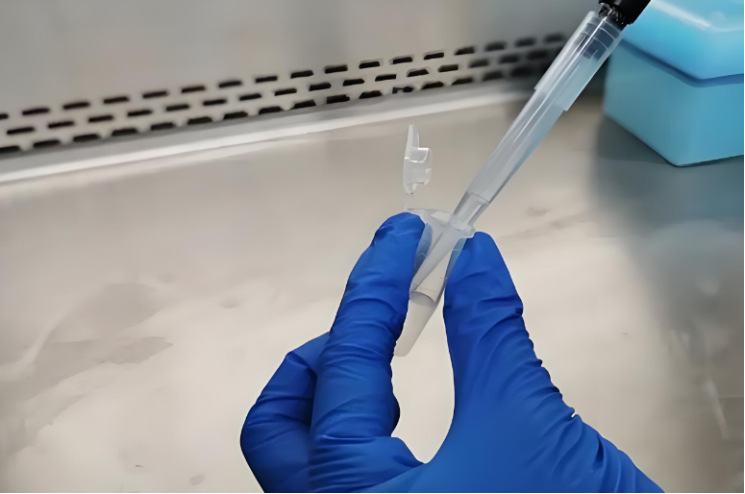
1. Preparation before calibration 1. Suitable calibration environment: Ensure that the calibration environment is clean, dust-free, and vibration-free. The temperature is controlled at 2025°C and the humidity is controlled at 5070% RH to ensure the accuracy of the calibration results. 2. Prepare calibration tools: (1) Calibration solution: usually water or a solution of known concentration, used for volume measurement in actual pipetting operations. (2) Clean pipette tip: Make sure the tip has no residue and no contamination. (3) Electronic balance: The accuracy should meet the experimental requirements and is used to measure the quality of the liquid absorbed by the pipette. (4) Timer: used to record the time when the pipette absorbs and discharges liquid. (5) Calibration certificate: A document used to record the calibration results and date for subsequent reference. 3. Check the status of the pipette: (1) Make sure that the pipette is not damaged in appearance, has no leakage, and that all parts are intact. (2) Check whether the pipette's volume adjustment knob is flexible and whether the pipette tip is installed tightly.
2. Calibration steps 1. Volume calibration: (1) Adjust the pipette to the required range, such as 100 μL, 200 μL, etc. Turn counterclockwise to increase the range; turn clockwise to decrease the range. It is necessary to ensure that the adjustment is from the large range to the small range to the test point. If the adjustment is accidentally lower than the test point, the adjustment wheel needs to be turned counterclockwise for at least half a turn, and then adjusted to the test point. (2) Use a pipette to absorb the standard solution, be careful to avoid bubbles, and pay attention to the standardization of the operating process. (3) Discharge the standard solution in the pipette into a container of known mass, and immediately record the mass of the container at this time. (4) Repeat the above operation at least three times and calculate the average volume removed each time. (5) Compare the average volume with the set value of the pipette and calculate the error value. If the error is within the allowable range (usually ±2%), the calibration is qualified; otherwise, the pipette needs to be adjusted or replaced. 2. Repeatability calibration: (1) Set the aspiration volume of the pipette to ensure that it is within the commonly used range. (2) Perform multiple (such as 10) liquid suction and discharge operations continuously. (3) Use the calibration solution to measure the volume of each pipette, and calculate the average value and coefficient of variation. (4) Determine whether the repeatability is qualified according to the manufacturer's specifications. If the repeatability error exceeds the allowable range, the pipette needs to be adjusted or repaired. 3. Leak calibration: (1) Fill the pipette with calibration solution and wait for 1 minute to observe whether there is leakage. (2) If there is leakage, check the sealing of the pipette and adjust or replace it.
3. Calibration result recording and analysis 1. Record calibration results: During the calibration process, record the data of each calibration in detail, including calibration date, calibration personnel, pipette model, serial number, range setting, actual pipetting volume, and error value information. 2. Analyze calibration data: perform statistical analysis on the data obtained during the calibration process, and calculate error values and repeatability errors. Based on the error value and repeatability error, determine whether the pipette needs adjustment or repair. 3. Issue a calibration certificate: After the calibration is passed, a calibration certificate will be issued, indicating the calibration status and validity period of the pipette.
4. Calibration cycle and maintenance 1. Establish a calibration cycle: Develop an appropriate calibration cycle based on the frequency of use in the laboratory and the performance of the pipette. Calibration is usually recommended on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. 2. Routine maintenance: When using the pipette, avoid applying excessive force or collision to avoid damage. Clean pipettes and calibration tools regularly to keep them dry and clean. For pipettes that do not meet the calibration requirements, they should be adjusted or repaired in time to ensure that their performance meets the experimental requirements.
5. Precautions 1. During the calibration process, the manufacturer's recommended methods should be strictly followed. 2. The calibration fluid should be kept clean to avoid contamination. 3. Avoid creating bubbles when the pipette absorbs and discharges liquid, so as not to affect the accuracy of the calibration results. 4. During the calibration process, attention should be paid to keeping the pipette vertical and avoiding tilting or shaking.
By following the above standard operating procedures for pipette calibration, we can ensure that the pipette performs accurately and highly reliably in every operation, which provides a solid guarantee for the accuracy of experimental results. Therefore, every calibration work should be performed with a rigorous attitude and precise operations to ensure that every step of the process strictly complies with the requirements of the procedures and that every recorded data is accurate.
Related reading recommendations
8 laboratory automation complaints about PI errors
OT-2 liquid handling robot safety and regulatory compliance information
3 ways automation can lead to better biological laboratory results
Methods for plasma sample preprocessing
opentrons flex fully automatic pipetting workstation
The difference between automated pipetting workstations and manual operations
The experienced service team and strong production support team provide customers with worry-free order services.

简体中文

繁體中文

English

日本語

한국인