-
article · 2026Year28Moon3Day
Opentrons Flex 的节省成本优势与投资回报分析
Read More -
article · 2026Year24Moon3Day
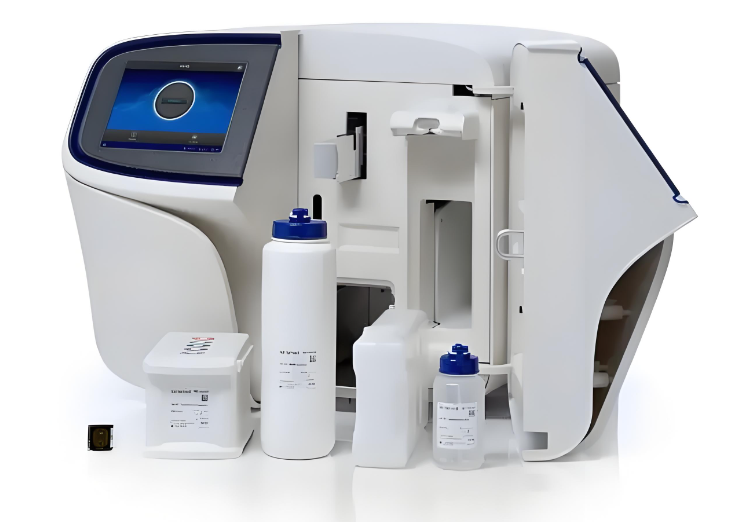
使用 Opentrons Flex 降低 NGS 文库制备误差的方法
Read More -
article · 2026Year8Moon2Day
高通量 NGS 自动化技术趋势:Opentrons Flex 的作用
Read More


Any advanced technology has its two sides. Next-generation sequencing (NGS), as an important tool in modern biological research, while demonstrating its unparalleled advantages, is also accompanied by some problems that cannot be ignored. Limitations, this article will conduct a detailed analysis of its advantages and disadvantages:
1. Advantages
1. High throughput:
NGS can process millions or even billions of DNA molecules simultaneously, greatly improving sequencing throughput. This makes it possible to sequence a large number of samples in a short time, accelerating the process of scientific research.
2. High accuracy:
By introducing innovative technologies such as reversible termination ends, NGS achieves sequencing while synthesis, thereby improving sequencing accuracy. This high accuracy is important for detecting genetic variations, disease-related genes, etc.
3. Low cost:
With the continuous advancement of technology and the popularization of platforms, the cost of NGS sequencing has gradually decreased. This enables more laboratories and research institutions to afford sequencing and promotes the widespread development of scientific research.
4. Wide application:
NGS technology is widely used in many fields such as genomics, transcriptomics, and epigenetics. It can not only be used for basic research such as detecting genetic variation and regulating gene expression, but can also provide important support for disease diagnosis, drug research and development, crop breeding, etc.
5. High flexibility:
The NGS platform supports multiple types of sequencing experiments, including whole-genome sequencing, exome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, etc. This allows researchers to select appropriate sequencing strategies based on specific research needs.
2. Disadvantages
1. Short reading length:
Compared with traditional Sanger sequencing, the read length of NGS is relatively short, generally no more than 500bp. This limits its use in certain applications that require long-read sequencing, such as the detection of complex structural variants.
2. Large amount of data and complex analysis:
The amount of data generated by NGS is huge, which places high demands on computing resources and storage space. At the same time, the analysis of data is also relatively complex and requires professional bioinformatics knowledge and tools for processing.
3. High error rate:
Since there are many possible sources of errors in the NGS sequencing process (such as PCR amplification errors, sequencer errors, etc.), the error rate of its sequencing results is relatively high. This requires error correction and quality control through certain algorithms and strategies.
4. High requirements for sample quality:
NGS has high requirements for sample quality. If there are many problems such as degradation, contamination, or impurities in the sample, the accuracy and reliability of the sequencing results may be affected.
5. High technical threshold:
NGS technology involves many complex steps and links, including library construction, sequencing reactions, data analysis, etc. This requires researchers to have high experimental skills and bioinformatics knowledge to successfully carry out relevant research.
Second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology has significant advantages such as high throughput, high accuracy, and low cost, but it also has limitations such as short read length, large data volume, and high error rate. Therefore, in practical applications, it is necessary to select appropriate sequencing strategies and technology platforms based on specific research needs and experimental conditions.
The experienced service team and strong production support team provide customers with worry-free order services.

简体中文

繁體中文

English

日本語

한국인