-
 article · 2025Year42Moon11Day
article · 2025Year42Moon11Day什么是 Opentrons Flex PCR 工作站?
Read More -
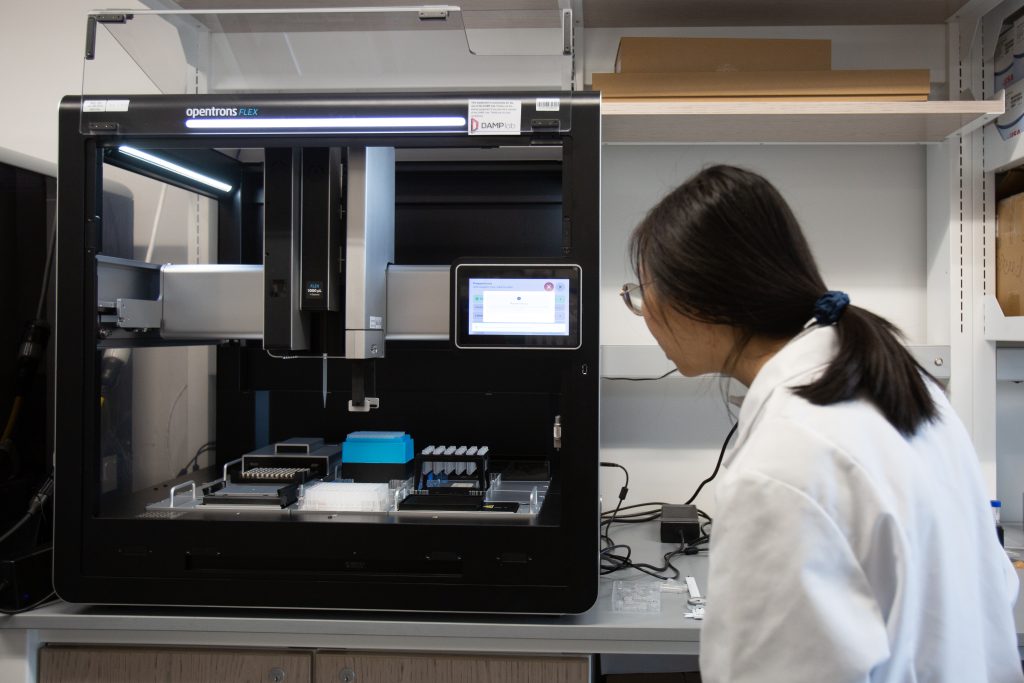 article · 2025Year38Moon11Day
article · 2025Year38Moon11DayOpentrons Flex PCR 工作站适合哪些实验室?
Read More -
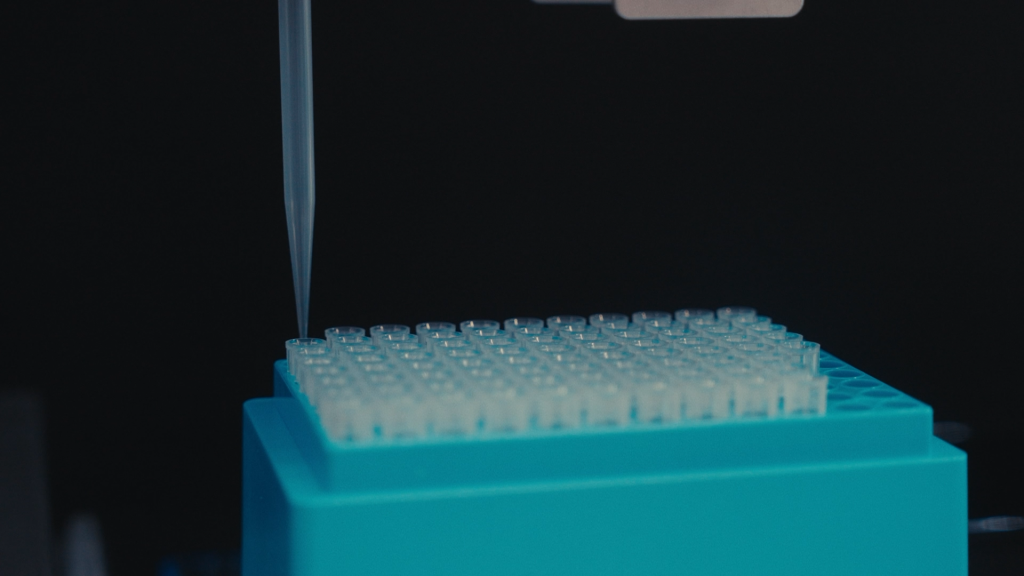 article · 2025Year58Moon10Day
article · 2025Year58Moon10Day移液器在生物实验中的关键作用与应用场景
Read More


A protein purification system is a device used to isolate and purify target proteins from complex biological samples. It can effectively separate the target protein from other impurities in the mixture, thereby meeting the demand for high-purity proteins in scientific research, pharmaceuticals, clinical diagnosis and other fields.

1. Principle The protein purification system mainly uses the following three basic principles for separation and purification: 1. Molecular sieve chromatography: also called gel filtration chromatography, which uses the network structure of gel to separate and purify molecules according to their size, shape, and charge. A method of separation based on differences in properties. When a mixture of proteins containing different relative molecular masses passes through a gel chromatography column, proteins with smaller relative molecular masses easily enter the channels inside the gel, so their movement distance is longer and their movement speed is slower; Larger proteins, on the other hand, cannot easily enter the channels inside the gel and can only move downward along the gaps between the gel particles. Therefore, their movement distance is shorter and their movement speed is faster. In this way, proteins with different relative molecular masses are separated. 2. Affinity chromatography: It is a method that uses the specific affinity between proteins and certain ligands for separation. Usually, a ligand with affinity is connected to the carrier of the chromatography column to form an affinity chromatography column. When the mixture containing the target protein passes through the affinity chromatography column, the target protein will bind to the ligand and be adsorbed on the column; other impurities cannot bind or have weak binding force and flow out with the eluate. Then, by changing the ionic strength, pH value of the eluent, or adding a stronger ligand binding solution, the bound target protein is eluted from the column, thereby achieving purification. 3. Ion exchange chromatography: It is a method that uses differences in protein surface charges for separation. The carrier in the ion exchange chromatography column has exchangeable ionic groups. When the mixture containing protein passes through the chromatography column, the protein will exchange with the ionic groups on the carrier and be adsorbed on the column. Since different proteins have different charge properties and amounts, their binding forces to ionic groups on the carrier are also different. By changing the ionic strength and pH value of the eluent, proteins with different binding strengths can be eluted from the column in sequence, thereby achieving separation and purification.
2. Application Protein purification systems are widely used in the following fields: 1. Biopharmaceuticals: In the drug development process, protein purification systems are used to produce recombinant protein drugs, such as antibodies, hormones, enzymes, and vaccines. The purity of these drugs is critical to their efficacy and safety, so protein purification systems have broad application value in this field. 2. Clinical diagnosis: Protein purification technology can be used to prepare antibodies and other protein reagents for disease marker detection. These reagents are of great significance for early diagnosis and condition monitoring of diseases, and can help doctors develop more effective treatment plans. 3. Basic biological research: Scientific researchers use protein purification systems to obtain high-purity proteins for structural biology research, functional analysis, interaction research, etc. These studies help reveal the mechanism and regulation of proteins in life processes and provide important support for the development of life sciences. 4. Food industry: In food processing, protein purification can be used to extract and purify food-grade proteins, such as whey protein and soy protein. These proteins can be used as nutritional supplements or food additives to improve the nutritional value and taste of food. 5. Agriculture: Protein purification technology is used in agricultural biotechnology to produce protein products for plant disease control and growth promotion. These products can help farmers improve the yield and quality of crops and promote sustainable agricultural development. 6. Environmental science: In environmental monitoring and pollution treatment, protein purification systems can be used to extract specific proteins for detecting pollutants or as bioremediation agents. These proteins have important application value in environmental pollution control and ecological protection.
In the study of protein purification, we can see that this technology is not only the basis of modern biotechnology, but also plays an important role in the progress of life sciences. Using methods such as molecular sieve chromatography, affinity chromatography, and ion exchange chromatography, protein purification systems can efficiently and accurately extract and purify target proteins from complex biological samples. This provides strong support for scientific research, drug development, clinical diagnosis, industrial production and other fields.
Related reading recommendations
Introduction to Opentrons pipette temperature control module
Introduce automation into your laboratory
3 ways automation can lead to better biological laboratory results
Application of fully automatic pipetting workstation in cell culture
Thermal oscillation module GEN1 instruction manual
The embodiment of fully automatic pipetting workstation in robotic technology
The experienced service team and strong production support team provide customers with worry-free order services.

简体中文

繁體中文

English

日本語

한국인