-
article · 2025Year8Moon17Day
Opentrons Flex 使用中常见问题有哪些?
Read More -
article · 2025Year5Moon16Day
如何通过 Flex 提高蛋白质组学实验产能?
Read More -
article · 2025Year59Moon16Day
Opentrons Flex 的模块化设计是否有利于实验扩展?
Read More


Pipettes are an indispensable and important tool in laboratories in fields such as biology, chemistry and medicine. It helps researchers transfer and distribute liquid samples accurately, which is critical to the accuracy and reliability of experimental results. Among them, 8-channel pipettes have been widely used in high-throughput experiments due to their high efficiency and speed. However, in order to ensure the accuracy and traceability of experimental data, it is particularly important to calibrate the 8-channel pipette regularly.
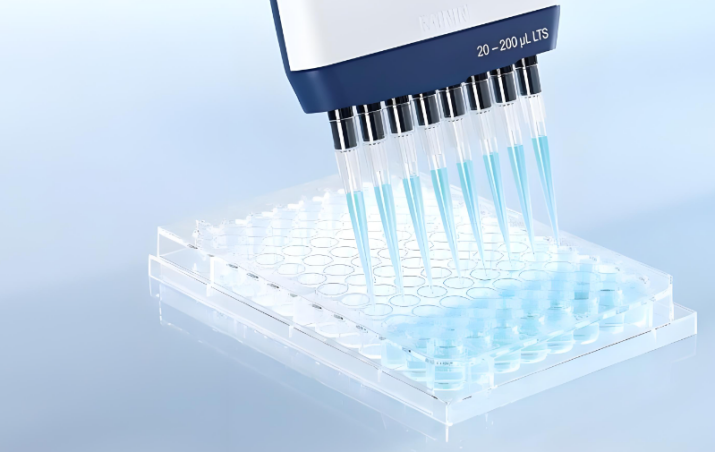
1. Preparation stage 1. Clean the pipette: Before performing calibration, ensure that the inside and outside of the pipette are clean and free of residues or contaminants. 2. Prepare calibration solution: Select an appropriate calibration solution, usually distilled water, ethanol or other standard solutions of known concentration or volume. 3. Prepare calibration tools: This may include balances, thermometers, timers, calibration stands, standard containers, etc. 4. Check the condition of the pipette: Make sure that the pipette has no obvious damage or wear and that all parts (such as tips, pistons, etc.) are in good condition.
2. Perform calibration 1. Set the pipette: Set the pipette to the volume scale that needs to be calibrated. 2. Aspirate calibration solution: Use a pipette to absorb a certain amount of calibration solution, be careful to avoid air bubbles, and ensure that the aspirated volume is consistent with the set value. 3. Discharge the calibration solution: Discharge the absorbed calibration solution into the standard container. Pay attention to the uniform discharge speed to avoid splashing or residue. 4. Measure the calibration solution: Use a balance or other measuring tools to measure the mass or volume of the calibration solution in the standard container, and calculate the actual volume removed based on the density of the solution. 5. Record data: Record all data during the calibration process, including pipette settings, actual pipetted volumes, results of measurement tools, etc. 6. Repeated calibration: It is usually necessary to perform multiple calibrations on each scale to improve the accuracy and reliability of the results.
3. Analyze the calibration results 1. Calculate the error: Compare the actual pipetted volume with the pipette setting value and calculate the error. 2. Evaluate the calibration results: Evaluate whether the calibration results are qualified based on the calibration standards provided by the manufacturer or the laboratory's internal standards. 3. Record the calibration results: Record the calibration results on the calibration record sheet or calibration certificate, including the calibration date, calibration personnel, calibration results and other information.
4. Follow-up processing 1. Adjust the pipette: If the calibration result is unqualified, the pipette needs to be adjusted until it reaches the calibration standard. 2. Mark the calibration status: Mark the calibration status on the calibration certificate or pipette, such as "qualified", "unqualified", etc. 3. Regular calibration: According to the requirements of the laboratory or the frequency of use of the pipette, develop a calibration plan to ensure that the pipette always maintains accuracy and reliability.
5. Calibration method 1. Volume calibration: Adjust the pipette to the required range, such as 100μL, 200μL, etc. Use a pipette to draw up the standard solution, taking care to avoid bubbles. Discharge the standard solution from the pipette into a container of known mass and immediately record the mass of the container at this time. Repeat the above steps at least three times and calculate the average volume pipetted each time. Compare the average volume with the set value of the pipette. If the error is within the allowable range (usually ±2%), the calibration is qualified; otherwise, the pipette needs to be adjusted or replaced. 2. (Optional) Gravity calibration: Adjust the pipette to the required range. Use a pipette to aspirate the standard solution, also taking care to avoid air bubbles. Record the time it takes for the pipette to aspirate the liquid (t1). Gently squeeze the button on the pipette to slowly discharge the liquid into a container of known mass, and record the mass of the container (m2) and the time for discharging the liquid (t2). Calculate the volume pipetted according to the formula and repeat this process at least three times to calculate the average volume. Compare the average volume with the pipette setting value to determine whether the calibration is qualified.
During the calibration process, we must not only pay attention to the standardization of technical operations, but also pay attention to details, such as avoiding contamination, maintaining temperature stability, using appropriate tips, etc. These are key factors to ensure the accuracy of calibration results. At the same time, regular calibration and recording of calibration results are also important means to maintain the accuracy and reliability of pipettes.
Related reading recommendations
Opentrons pipette thermal cycling module GEN2
Handling robot instrument service overview
Automated determination of hydrogen peroxide levels in THP-1 cells on OT-2 poster
The correct way to use the pipette
OT-2 liquid workstation operation interface
Basic steps and methods for programming Opentrons liquid workstation
The experienced service team and strong production support team provide customers with worry-free order services.

简体中文

繁體中文

English

日本語

한국인